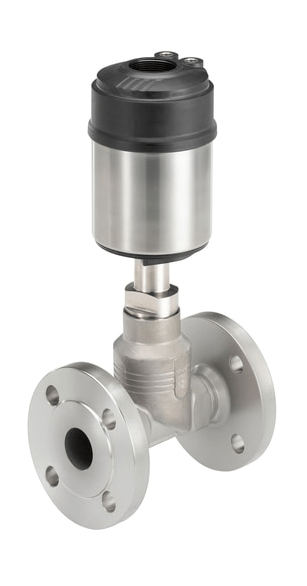
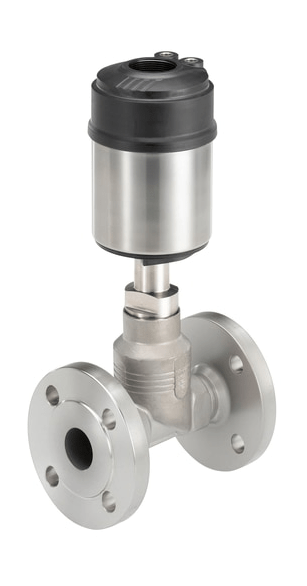
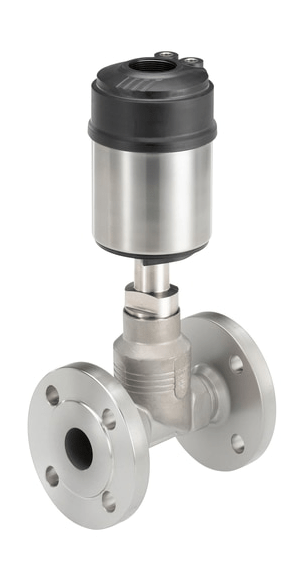
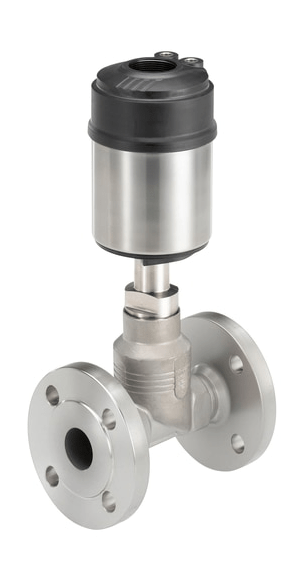
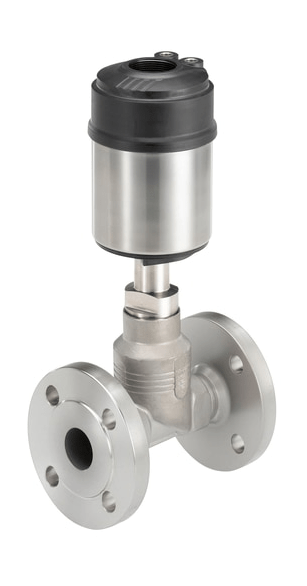
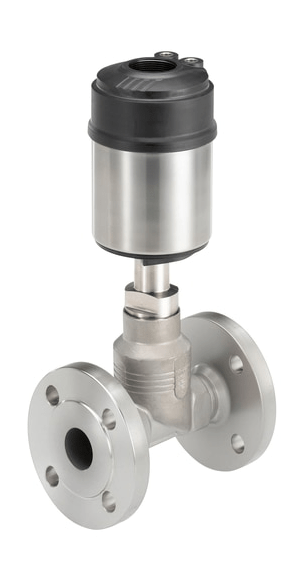
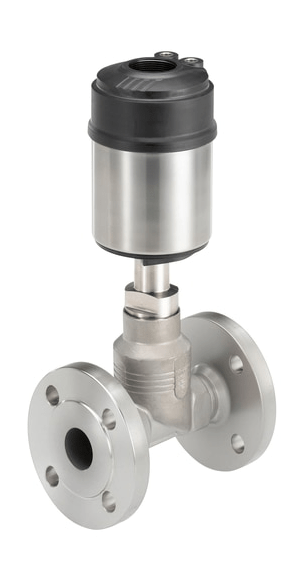
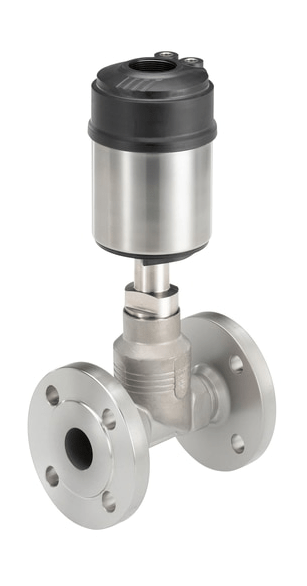
Pneumatic valves
Pneumatic valves are widely used to perform various operations with compressed air: its intake into certain elements of the switch and release from them, intake into the arc extinguishing device, release (discharge) at a certain point in time, restriction or termination of its supply, etc.
The valves, i.e. their opening and closing, are controlled either mechanically or by compressed air. In accordance with this, according to the control method, the valves are divided as follows:
- valves with mechanical control, in which the movement of their moving parts is performed by some extraneous force acting on the valve stem, for example, by hand, an electromagnet, a pneumatic actuator, etc.;
- valves with pneumatic control, in which the movement of their moving parts is carried out by compressed air.
According to their purpose, valves are divided into the following types:
- launchers that supply a small amount of air at the start of the operation (on or off); they are opened by an electromagnet or a start button;
- blowholes designed to supply compressed air to or release from an arc extinguishing device;
- auxiliary.
The pneumatic valves are triggered by a pneumatic or electropneumatic signal. The principle of operation of valves with pneumatic actuator is determined by two conditions. NC - normally closed design: the valve is closed if the pressure on the actuator is not applied and opens when pressure is applied. BUT - normally open design, when the pressure is not applied, the valve is open, and when the control pressure is applied, the valve closes.
Pneumatic valves are used in various industries and farms to control the flow medium in pipelines.
Pneumatic valves are used in systems with extensive compressed air networks and compressors. Compressed air, oils, lubricants, water, steam, etc. can serve as the working medium of such valves. The type of working medium depends on the sealing material in the valve.