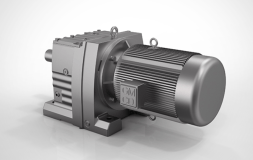
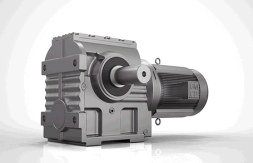
Cycloidal gear motors
Cycloid pinion gear motor
A cycloidal coaxial gearbox operating on the principle of a planetary drive with a small tooth difference, as well as gearing cycloid pinwheel, is an innovative transmission equipment and drive gearbox, widely used in the field of textile printing, light and food industries, metallurgy, mines, petrochemical industry, lifting and transport, engineering equipment, etc.
Specifications
- High standardized modular design
- High-grade materials ensure the durability of the product
- High strength, compact design
- Long Service life
- Low noise level
- High efficiency
- Large radial load capacity
- Axial load up to 5% of radial load
How does the planetary gear reducer work?
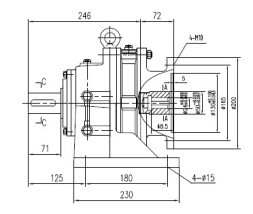
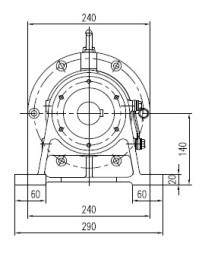
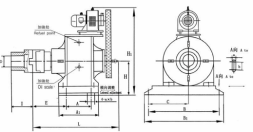
The rotation from the electric motor is transmitted by means of an involute transmission to the eccentric shafts of the cycloid discs. Depending on the gearbox size and its design, there may be two or three eccentric shafts.
Needle bearings are mounted on eccentric shafts , on the outer cage of which cycloid discs are supported. Cycloid discs are supported through roller angular contact bearings on the input shaft and on the flange of the gearbox. Cycloidal discs perform a complex movement – plane-parallel rotation and rotation around their axis. At the same time, the peripheral surface of the disks describes a mathematical curve – a cycloid, which is where the second (Europeanized) name of this type of gearboxes came from. Making such a complex movement, the pins (teeth of the cycloid gear) enter the corresponding slots on the gearbox housing. The eccentric shafts spun by the input shaft of the gearbox around their axis due to the plane-parallel movement of the cycloidal discs are forced to move along a concentric circle in space, thereby turning the flange of the output shaft of the gearbox.
The use of planetary gearboxes
The principle on which the cycloid gearbox works was back at the beginning of the last century. However, the level of technology at that time did not allow manufacturing parts with the required accuracy. Now, taking full advantage of the capabilities of modern technological equipment, it is possible to realize the key advantages that distinguish the cycloidal gearbox. Exactly:
- High efficiency, up to 90%. And, therefore, low friction and heating losses;
- The possibility of implementing both very low and very high gear ratios in one stage;
- The minimum possible number of steps, which entails record compactness and minimum weight;
- Low noise level and low moment of inertia;
The load distribution inside the gearbox allows for high wear resistance and the ability to withstand fivefold overloads compared to the rated torque.
There are many design options Cycloid gearbox: A high-speed shaft rotates two or three eccentrics that roll cycloidal discs along the inner surface of the gearbox housing. The more correct name for the teeth of cycloidal discs is caps, hence their second name – planetary gearboxes.
If, during rolling, the cycloidal discs move clockwise inside the gearbox housing, then at the same time they slowly rotate counterclockwise around their own axis.
This rotation is transmitted to the output shaft of the gearbox by means of the drive pins. The gear teeth of conventional gearboxes work on bending. The elements of the pinion gearbox work on compression, which causes a significantly higher margin of safety. Besides, the configuration of the cycloidal discs and the inner surface of the stationary gear ring ensures simultaneous contact of up to 66 at any given time% teeth. This fact causes high resistance to shock overloads, reaching 500% of the nominal